Anleitungen & Know-How
Von Zeit zu Zeit erstellt unser BLANKOM-Team nützliche technische Whitepapers und Beschreibungen für verschiedene Anwendungsfälle.
Diese Dokumente werden hier veröffentlicht und sind sehr hilfreich, um technische Basisinformationen bis hin zu fortgeschrittenen Erklärungen für DVB,
Streaming, Encoding / Codecs und IPTV zu erhalten.
Die meisten PDF-Dokumente sind in Englisch da wir viel mit Projekten und Kunden /
Systemintegratoren aus dem Ausland zusammenarbeiten.
Einige sind auch 2-sprachig: DE/EN _____ Schauen Sie also bitte regelmäßig vorbei - wir freuen uns...
LINK zum PDF: ->
DE: Hilfreiche Erklärungen und ein Leitfaden über moderne digitale Videotechnik und ihre Begriffe: VBR/CBR, FPS, interlaced (i)/progressive (p)...
LINK zu der Seite: -> zu der Web-Seite:
LINK zum PDF: -> DE: Eine kurze Beschreibung über Streaming - Was is dat überhaupt?
Link zu Video-Encoder -Streamer Tipps und Tricks: Tipps und Tricks Seite für SoC Multiprotocol-Encoder
Was ist Transcoding? ...

Über Video zu IP-Encoder, -Codecs und Aufnehmen/Recording - deutsch-english
- IP streaming and recording made easy
- HDMI streaming encoder with recording function
- h.265 and h.264 Video Encoding - What are the differences?
- H.264 is still one of the most frequently used video formats today
- What is H.264?
- Encoding and decoding with H.264 - How HDMI IP streaming works with H.264
- H.264 applications - When and where can this format be used?
- The difference between H.265 and H.264
- AV devices with integrated H.265 hardware decoder
- Comparison between H.265, H.264 and MPEG-2
- Advantages of using H.265/ H.264 encoders and decoders

Ein “Whitepaper” von Satelliten - Empfangstechnik bis zur
Handlungshilfe um Hospitality IPTV Systeme zu konzipieren - English
- Preface
- So before you “IPTV”:
- A small note about PAY-TV and streaming
- Satellite reception and distribution
- Modern SAT- technology: With fibre SAT-distribution optic systems
- Coming back to the REDUNDANCY
- The IPTV Headend
- Design a Headend:
- Collecting your Satellite Transponders
- Headend Components
- DVB is ‘somehow’ complex: TS ... CC-Errors...
- Deciding the Headend- CLASSES
- The output streams, IGMP, Encoding, Transcoding
- SetTopBoxes, Digital Signage (DS)
- The final step is the question of additional services for your IPTV system ...

TCP/IP Unicast… streaming protocols und IGMP - German/English
Multicast und IGMP:
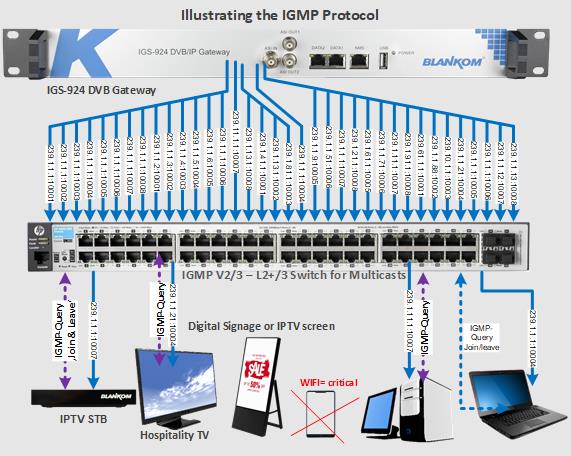
Zeichnung zur Arbeitsweise von IGMP
Der Unterschied zwischen IGMP und Snooping / The Difference between the full IGMP-Version and IGMP-Snooping in DE/EN
A whitepaper about Streaming Protocols -EN PDF
- VIDEO OVER IP PROTOCOLS
- RTP & RTCP
- HTTP ADAPTIVE STREAMING PROTOCOLS
- MULTI-BITRATE ENCODINGS
- LOW LATENCY HTTP ADAPTIVE STREAMING
- RTMP
- ZIXI PROTOCOL
- SRT
- Reliable Internet Stream Transport (RIST)
- QUIC
- REPLACING SDI WITH IP
- ATSC 3.0 AND ROUTE
- RECOMMENDATIONS
- A small overview by 3rd party IP-Cores about implementation of different Streaming relevant technologies/protocols in software (FPGA/SoC)
A Technical Overview about the Streaming Protocol SRT PDF-EN
Eine Einführung in den MPEG-Transport-Stream - english
Eine Erklärung zur Latenzzeit - A Guide to Low Latency in live streaming
Eine Anleitung zu 'Encoding' ...A Guide to Encoding and crack points of Low Latency Streaming:
About Adaptive Bitrate Streaming - was ist das ?
Applicationsbeispiele: Transcoding in Hospitälern, UHD injection in KabelTV DVB-C Channels, HDMI extending, Video encoder und OBS:
Applikations-Beispiel (DE/EN): Transcoder Anwendung in Krankenhaus-TV Systemen mit dem BTR-6000: Kosten sparen durch Vermeidung des Austausches der Betten-TV's
Schnipsel:
Kranken- und Kurhäuser, Gefängnisse, Seniorenresidenzen und Wohnheime sowie auch ältere
Hotelbauten sind ein typischer Anwendungsfall wenn es darum geht, eine bestehende Telefon-
Infrastruktur (2-Drahtleitung) für die multimediale Versorgung der Betten bzw. Zimmer zu benutzen
ohne ein
- neues KabelTV Netz oder
- ein Gigabit-Ethernet Netzwerk
verlegen zu müssen.
Applikations-Beispiel (DE/EN): Wie man einen zusätzlichen (oder Info-) UHD-Kanal in ein existierendes Kabel-Netz einspeist z.B. als einen Extra Informations-Kanal in bestehende TV-Kabelnetze - Seniorenheime, Hotels, Kasernen, Kreuzfahrt-Schiffe, Gefängnisse, ...
EN: How to Extend an Ultra-HD or 4K HDMI-Signal
deutsch:
HDMI war ursprünglich als Verbrauchernorm gedacht, während SDI als Industrienorm bezeichnet wurde.
Aus diesem Grund unterstützt HDMI von Haus aus keine großen Kabellängen,
vor allem, wenn die Auflösungen über 1080p hinausgehen. SDI kann bis zu 100 m Kabellänge in
1080p50/60 (3 Gbit/s), während HDMI bei der gleichen Bandbreite maximal 15 m lang sein kann.
Es gibt mehrere Möglichkeiten, HDMI über diese 15 m hinaus zu verlängern. In diesem Artikel sprechen wir über
die gängigsten Methoden zur Verlängerung eines HDMI-Signals.
...
Auszug EN:
HDMI 4has initially been intended as a consumer standard, while SDI was designated as an
industry standard. Because of this, HDMI natively doesn’t support long cable lengths,
especially when the resolutions go beyond 1080p.
SDI can run up to 100m in cable length in
1080p50/60 (3 Gbit/s), while HDMI can stretch to a maximum of 15m in the same bandwidth.
There are several ways of extending HDMI beyond that 15m. In this article, we’ll talk about
the most common methods of extending an HDMI signal.
...
Aufnehmen/Recording von Video-Streams per OBS: How to connect our SoC Video-Encoder to OBS: Open Broadcaster Software ---> https://obsproject.com/de
Unicast vs. Multicast (Mit Dank an wikipedia):
Es gibt zwei Methoden der Datenübertragung vom Streaming-Server des Senders zum IPTV-Empfangssystem:
Unicast:
Bei Unicast steht jedem Zuschauer ein individueller Datenstrom zur Verfügung. Dadurch kann der Zuschauer den Startpunkt einer Sendung oder eines Videoclips (Video-on-Demand-Dienst) individuell bestimmen. Dies führt gleichzeitig zu einer erhöhten Netzbelastung, da jeder Stream Bandbreite benötigt.
Multicast:
Beim Multicasting erhalten alle Empfänger die gleichen Daten vom Sender zur gleichen Zeit. Das bedeutet, dass zunächst nur eine lineare Ausstrahlung möglich ist (linear, weil die Reihenfolge der Ausstrahlungen vom Nutzer nicht beeinflusst werden kann). Dies entspricht im Wesentlichen dem Prinzip des Broadcasting. Multicast hat gegenüber Unicast den Vorteil, dass die Netzbelastung für den Sender nicht mit der Anzahl der Teilnehmer zunimmt. In Empfängernetzen hingegen steigt die Netzlast erheblich. Ein Video-on-demand-Dienst ist jedoch nicht möglich. Als Kompromiss ist es möglich, einen Near-Video-on-Demand-Dienst anzubieten, bei dem das Video wiederholt zeitlich verschoben wird. Die maximale Wartezeit für ein Video ist dann der zeitliche Abstand der Wiederholungen.
Einige hilfreiche Übersichten/Poster über MPEG2-DVB-ATSC Tabellen und ihre Inhalte:

MPEG2- DVB-Broadcasting Übersicht und so...

MPEG2- DVB-Broadcasting Tabellen und so...

ATSC PSIP Tabellen und so...
Thanks to Tektronix and JDSU
13/18V Vert/Hor polarization switching (Sat)
22 kHz High/Low Band switching (Sat)
64QAM Quadrature Amplitude Modulation with 64 states
ADC Analog-Digital Converter
ADPCM Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation
ADR Astra Digital Radio
ADSL Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line
AES Audio Engineering Society
AF Adaptation Field
AIT Application Information Table (used for MHP)
AM Amplitude Modulation
API Application Programming Interface
ARD Arbeitsgemeinschaft der öffentlich-rechtlichen Rundfunkanstalten in Deutschland
ASCII American Standard Code for Information Interchange
ASI Asynchronous Serial Interface Standard DVB interface for Transport Stream
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode
ATSC Advanced Television Systems Committee
ATV Advanced TeleVision North American standard for Digital Broadcasting
BER Bit Error Ratio
Block (used for DCT) 8x8 pixels (JPEG, MPEG)
Bouquet
Set of services provided by the same operator on a network. The
bouquet is controlled by one single authority and sold as one single
entity.
BAT Bouquet Association Table. Table describing a
bouquet of programs offered by a broadcaster.
BTA Broadcasting
Technology Association
CA Conditional Access
CCITT Comité
Consultatif Internation Téléphonique et
Télégraphique
(1993>ITU-T)
CENELEC Comité Européen de Normalisation
ELECtrotechnique
C/I Carrier-to-Interference-Ratio (dB)
CAT
Conditional Access Table (PID=0x1) Reference to scrambled
programs.
CATV Community Antenna TV (sometimes thought to be
Cable TeleVision). The distribution of multiple TV channels to
subscribers via a cable network.
CEI/IEC Commission
Electrotechnique Internationale / International Electrotechnical
Commission
CEPT European Conference of Postal and
Telecommunications Administrations
CSA Common Scrambling
Algorithm
D/A Digital-Analog
DAT Digital Audio Tape
DAVIC
Digital Audio Visual Council
DBS Direct Broadcasting
Satellite
DSNG Digital Satellite News Gathering
DSR
Digital Satellite Radio
DSS Digital Satellite System
DTG
Digital TV Group
DTH Direct To Home Satellite digital
broadcasting services
DTVB Digital TeleVision
Broadcasting
DVB-MG DVB-Measurement Group
DVB-MS Digital
Video Broadcasting-Microwave Satellite Based. Terrestrial
broadcasting of TV signals to digital standard via microwave (f>10
GHz)
CIF Common Intermediate Format 360x288 @ 30 Hz
C/N or
CNR Carrier-to-Noise-Ratio (dB)
COFDM Coded Orthogonal
Frequency-Division Multiplex
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check
DAB
Digital Audio Broadcasting
DAC Digital-to-Analog
Converter
DAPSK Differential Amplitude Phase Shift Keying
DCT
Discrete Cosine Transformation Temporal to frequency transform
(JPEG/MPEG)
DigiTAG Digital Terrestrial TV Action
Group
Downlink Communication link satellite earth
DSM
Digital Storage Media. Flag in PH. Provide the capability of trick
modes (Fast Forward/Reverse)
DSM-CC Digital Storage Media
Command and Control. ISO/IEC standard developed for the delivery of
multimedia broadband services.
DTS Decoding Time Stamp
DTS
Digital Theater Systems Digital Surround is an audio encoding format
similar to Dolby Digital
DTT Digital Terrestrial
Television
DVB-C Digital Video Broadcasting -Cable Broadcasting
TV signals to a digital standard by cable. The RF spectrum in digital
cable TV networks has a frequency range of (approx.) 46 MHz to 850
MHz.
DVB Digital Video Broadcasting. European consortium that
has
standardized digital TV broadcasting.
DVB-MC Digital
Video Broadcasting-Microwave Cable Based.Terrestrial broadcasting of
TV signals to digital standard via microwave (f<10 GHz)
DVB-RCS
Digital Video Broadcasting-Return Channel Satellite
DVB-S
Digital Video Broadcasting -Satellite Broadcasting TV signals to
digital standard via satellite.
DVB-SMATV Satellite Master
Antenna TV
DVB-T /-T2 Digital Video Broadcasting -Terrestrial
Terrestrial broadcasting of TV signals to digital standard.
E/N
Energy per Bit/Noise in 1Hz Bandwidth
EBU European Broadcast
Union (UER)
ECL Emitter Coupled Logic
EDTV Enhanced
Definition TeleVision
EIT EIT for present and following
eventsP/F
EPG Electronic Program Guide Broadcasting data
structure that contains all the information describing the programs
and their events.
ES Elementary Stream. Data stream for video,
audio or data. Preliminary stage to PES.
ESCR Elementary Stream
Clock Reference
ETR ETSI Technical Report
ETR 290 ETSI
recommendation regarding measurement of MPEG-2/DVB TS
ETSI
European Telecommunication Standard Institute
GIF Graphics
Interchange Format
GigE Gigabit Ethernet
GOP Group Of
Picture
HDTV High Definition TeleVision
HEX HEXadecimal
(0x)
HFC Hybrid Fiber Coax Typical CaTV network
infrastructure
HTML Hypertext Markup Language
IEC
International Electrotechnical Commission
IEEE Institute of
Electrical and Electronics Engineers
IF
Intermediate Frequency. Generally 70 MHz for transmission. (950 to
1250 from the LNB)
ECM Entitlement Control Message This control
message transports a general key for Scrambling (Encryption).
EIT
Event Information Table, TV guide or EPG.
EMM Entitlement
Management Message This control message transports a personal key for
Scrambling (Encryption).
FEC Forward Error Correction Error
control bits added to useful data in the QAM/QPSK modulator (errors
may be detected and correct ed). I, Q In phase and Quadrature signals
(carrier digital modulation - phase and amplitude)
IRD
Integrated Receiver Decoder. Receiver with MPEG-2 decoder (Set Top
Box)
IRE Institute of Radio Engineers
IRT Institut für
RundfunkTechnik
IS International Standard
ISDN Integrated
Services Digital Network
ISO International Standardization
Organization
ITU International Telecommunications Union
Ku-Band
10.7-18 GHz (Satellite)
LDTV Low Definition TeleVision
LMDS
Local Multipoint Distribution System
LNB Low Noise Block. Also
called LNC (Low noise converter).
LTW Legal Time Window offset
Macroblock
(used for motion estimation) 16x16 pixels (JPEG, MPEG)
MCPC
Multiple Channels Per Carrier
MFN Multiple Frequency Network
(DVB-T)
MHP Multimedia Home Platform
MIP Megaframe
Initialization Packet Used by DVB-T to synchronize the
transmitters
MMDS Microwave Multichannel/Multipoint
Distribution System
MP@ML Main Profile at Main Level
MPTS
Mutliple Program Transport Stream. MPEG-2 TS containing several
programs that have been multiplexed.
JPEG Joint Photographic
Experts Group An ISO video compression standard for storage and
transmission of a variety of still graphics image formats
LED
Light Emitting Diode
LVDS Low Voltage Differential Signaling.
A balanced interface with a low signal voltage swing (about 300
mV).
MHEG Multimedia&Hypermedia information coding Expert
Group. Provides standards for the coded representation of multimedia
hypermedia information objects that are interchanged among
applications and services using a variety of media
MPE Multi
Protocol Encapsulation. Process using DVB table structures for the
Data transmission.
MPEG Moving/Motion Picture Experts Group An
ISO motion video/audio compression standard providing both lossy and
lossless compression.
Multiplex or Mux: To sequentially
incorporate several data streams into a single data stream in such a
manner that each may later be recovered intact.
MVDS Multipoint
Video Distribution System
NAB National Association of
Broadcasters
NIT Network Information Table Information about
orbit, transponder etc.
NVoD Near Video on Demand Same TV
program broadcasted simultaneously with a few minutes of starting
time difference
OFDM Orthognal Frequency Division
Multiplexing
ONID Original Network ID
OPCR Original
Program Clock Reference Assists in the reconstruction of a SPTS from
another Transport Stream.
OpenTV Application Program for EPG
(TPS/ARD/ZDF)
OSI Open Systems Interconnection
PAL Phase
Alternating Line Color TV System (Europe and 50 Hz countries)
PAT
Program Association Table (PID=0) List of all the programs contained
in TS Multiplex with reference to the PID of the PMT
PES
Packetized Elementary Stream Video and audio data packets and
ancillary data of undefined length.
PH PES Header
PID
Packet Identification Identification of programs/services in the
transport stream
PLL Phase Lock Loop
PRBS Pseudo-Random
Binary Sequence
PS Program Stream
P-STD Program System
Target Decoder
PSI Program Specific Information MPEG-2 Data
transmitted in TS for the de-multiplexer in the receiver
(PAT/PMT/CAT)
PTS Presentation Time Stamp Time stamp for vision
and sound, transmitted at least every 0.7 s. Integrated into
PES.
NTSC National TV Standard Committee Color TV System (USA
and 60 Hz countries)
PMT Program Map Table Reference to packets
with PCR, Name of programs, copyright, reference of the data streams
with PIDs etc. Belonging to the relevant program.
PCR Program
Clock Reference Reference for the 27-MHz clock regeneration.
Transmitted at least every 0.1 s.
STB Set Top Box. Digital TV
receiver (IRD)
QAM Quadrature Amplitude Modulation Type of
modulation for digital signals used in CaTV transmission(DVB-C).
Amplitude and phase of a carrier are modulated in order to carry
information.
QCIF Quarter Common Intermediate Format 180x144@15
Hz (Video telephony)
QEF Quasi Error-Free
QPSK Quadrature
Phase Shift Keying. Tpye of modulation for digital signals used in
satellite transmission (DVB-S).
RGB Red, Green, Blue
RLC
Run Length Coding Data compression method exploiting repetition
RS
Reed-Solomon. Protection Code 16-byte long error control code added
by the modulators to every 188 byte Transport Packets in a TS.
RST
Running Status Table
SAS Subscriber Authorization System
CA/SMS
SCPC Single Channel Per Carrier
SDI Serial Digital
Interface
SDT Service Description Table
SDTV Standard
Definition TeleVision
SER Symbol Error Rate
SFN Single
Frequency Network (DVB-T)
SI Service Information. All the DVB
data required by the receiver to demultiplex and decode the variety
of programs in the TS.
SIF Source Intermediate Format
360x288@25 Hz or 360x240@30 Hz (MPEG-1)
S-MATV, SMATV Satellite
Master Antenna TV
SMPTE Society of Motion Picture and
Television Engineers
SMS Subscriber Management System. In CA:
storage for customer data
SNG Satellite News Gathering.
Retransmission of events using mobile equipment and satellite
transmission (e.g. sports)
SNR or S/N Signal-to-Noise Ratio
SPI
Synchronous Parallel Interface. Standard DVB interface forTS.
SPTS
Single Program Transport Stream TS that contains one unique
program.
Statistical Multiplexer A device which combines a
number of time-varying bit streams into a single bit stream for
transmission.
ST Stuffing Table
SECAM Séquentiel Couleur
à Mémoire Color TV System (France, Eastern European countries)
General
Standards:
ETR
162: Allocation of Service Information codes for DVB systems
ETR
211: Guidelines on implementation and usage of service information
TR
101 290: Measurement guidelines for DVB systems
ISO/IEC
3818-1...4 and 6: Information Technology - Generic coding of moving
pictures and associated audio information: Part 1: Systems (ITU-T
H.222.0), Part 2: Video (Rec. ITU-T H.262), Part 3: Audio: Audio for
surround sound: Layer: L1, L2 (DVB, DAB, DVD), L3 (Mp3): MPEG-2
AAC
(Advanced Audio Coder): Surround Sound (Digital AM), Part 4:
Conformance test, Part 6: Extension for DSM-CC
MPEG-1 (ISO/IEC
11172-3): Audio for mono and stereo sounds
Dolby Digital AC3
(Audio Code N 3): For stereo surround
ISO/IEC 13818-9:
Information Technology - MHEG standard
ISO/IEC 14496:
Information Technology (MPEG-4). Very low bit rate audio-visual
coding
ISO 15938: Multimedia content description interface
(MPEG-7)
EN 101 192: DVB specification for data broadcasting
TR
101 202: Implementation Guidelines for Data Broadcasting
TS 101
812: DVB Multimedia Home Platform (MHP) Specification
DVB A010:
Interfaces (ASI/SPI) for CATV/SMATV Headends and Similar Professional
Equipment
ETS 300 421: DVB-S, channel coding and modulation for
11/12 GHz satellite services
ETS 300 429: DVB-C, channel coding
and modulation for cable systems
ETS 300 744: DVB-T, Digital
Terrestrial Transmission Systems
ETS 300 743: DVB subtitling
system
TS 101 191: DVB mega-frame for Single Frequency Network
(SFN) synchronization
ETS 300 468: Specification for Service
Information (SI) in DVB systems
ETS 300 472: Specification for
conveying ITU-R System B Teletex in DVB bit streams
ETS 300 473:
DVB Satellite Master Antenna Television (SMATV) distribution
systems
ETS 300 802: DVB Network independent protocols for
interactive services
EN 101 790: DVB-RCS; Interaction channel
for satellite distribution systems
TR 101 790: Guidelines for
the use of EN 301 790
EN 301 958: DVB-RCT; Interaction channel
for DTT incorporating Multiple Access OFDM
ES 200 800: DVB-RCC;
Interaction channel for Cable TV distribution systems (CATV)
ETR
154: DVP implementation guidelines for the use os MPEG-2 Systems,
Video and Audio in satellite, cable and terrestrial broadcasting
applications
SECA, Société Europ. de CA
TV TeleVision
TDT
Time and Date Table
TH Transport Stream Header
TIFF Tagged
Image File Format
TM Technical Module (DVB-Project)
TOT
Time Offset Table
Transponder Trans(mitter) and (res)ponder.
Equipment inside the satellite receiving and re-sending
information.
Transport Packet 188 byte packets organized in a
TS.
TS Transport Stream. Packet stream contains PES and PSI
belonging to one or several programs.
TS Header Transport Stream
Header. The first 4 bytes of each
TS packet contain the data
(PID) required for the demultiplexer in addition to the sync byte
(0x47). These bytes are not encoded.
T-STD Transport Stream
System Target Decoder
Uplink Communication link earth
satellite
UTC Universal Time Code
UER Union Européenne de
Radio-Télévision EBU
UHF Ultra High Frequency, 470 to 862
MHz
UIT Union Internationale des Télécommunications (ITU)
VBI
Vertical Blanking Interval
VBV Video Buffer Verifier (MPEG-2
Video)
VCO Voltage Controlled Oscillator
VDSL Very high bit
rate Digital Subscriber Line
VHF Very High Frequency, 47 to 300
MHz
VHS Video Home System
VLC Variable Length Coding. Data
compression method (Huffmann)
VoD Video on Demand
VPS Video
Programming System. Transport of recording controlcommands via a
dedicated television line.
Some
Conditional Access Vendor
Names:
Irdeto
BetaCrypt
Mediaguard
Viacces
Cryptoworks
Nagra
NDS
Videoguard
Conax
Cryptoworks
MediaCipher
Panaccess
Verimatrix
